MySQL. Table size
SELECT table_name AS table_name, engine, ROUND(data_length/1024/1024,2) AS total_size_mb, table_rows FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema=DATABASE(); //or justtable_schema='table_name';
SELECT table_name AS table_name, engine, ROUND(data_length/1024/1024,2) AS total_size_mb, table_rows FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema=DATABASE(); //or justtable_schema='table_name';
tar -cvfp file.tar dir
tar -xvfp file.tar
-p Restore the named files to their original modes,and ACLs if applicable,ignoring the present umask
Kernel Parameters:
| Parameter | Minimum Value | File |
|---|---|---|
semmsl |
250 | /proc/sys/kernel/sem |
semopm |
100 | |
semmni |
128 | |
semm |
32000 | |
shmall |
2097152 | /proc/sys/kernel/shmall |
shmmax |
Minimum: 536870912;
Maximum: A value that is 1 byte less than the physical memory Recommended: More than half the physical memory See My Oracle Support Note 567506.1 for additional information about configuring |
/proc/sys/kernel/shmmax |
shmmni |
4096 | /proc/sys/kernel/shmmni |
file–max |
6815744 | /proc/sys/fs/file-max |
ip_local_port_range |
Minimum: 9000;
Maximum: 65500 |
/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range |
rmem_default |
262144 | /proc/sys/net/core/rmem_default |
rmem_max |
4194304 | /proc/sys/net/core/rmem_max |
wmem_default |
262144 | /proc/sys/net/core/wmem_default |
wmem_max |
1048576 | /proc/sys/net/core/wmem_max |
aio-max-nr |
1048576;
Note: This value limits concurrent outstanding requests and should be set to avoid I/O subsystem failures. |
/proc/sys/fs/aio-max-nr |
| Parameter | Command |
|---|---|
semmsl, semmns, semopm, and semmni |
# /sbin/sysctl -a | grep sem This command displays the value of the semaphore parameters in the order listed. |
shmall, shmmax, and shmmni |
# /sbin/sysctl -a | grep shm |
file-max |
# /sbin/sysctl -a | grep file-max |
ip_local_port_range |
# /sbin/sysctl -a | grep ip_local_port_range |
rmem_default |
# /sbin/sysctl -a | grep rmem_default |
rmem_max |
# /sbin/sysctl -a | grep rmem_max |
wmem_default |
# /sbin/sysctl -a | grep wmem_default |
wmem_max |
# /sbin/sysctl -a | grep wmem_max |
/etc/sysctl.conf:
kernel.shmmax = 4294967295
# Maximum amount of shared memory (in pages) that can be used at one time on the system and should be at least ceil (SHMMAX/PAGE_SIZE)
kernel.shmall = 1048575
kernel.shmmni = 4096
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 9000 65500
net.core.rmem_default = 262144
net.core.rmem_max = 4194304
net.core.wmem_default = 262144
net.core.wmem_max = 1048576
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576
fs.file-max = 6815744
/sbin/sysctl -p
/sbin/sysctl -a
Resource Limit Recommended Ranges:
| Resource Shell Limit | Resource | Soft Limit | Hard Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open file descriptors | nofile | at least 1024 | at least 65536 |
| Number of processes available to a single user | nproc | at least 2047 | at least 16384 |
| Size of the stack segment of the process | stack | at least 10240 KB | at least 10240 KB, and at most 32768 KB |
Check the soft and hard limits for the file descriptor setting. Ensure that the result is in the recommended range. For example:
$ ulimit -Sn
4096
$ ulimit -Hn
65536
Check the soft and hard limits for the number of processes available to a user. Ensure that the result is in the recommended range. For example:
$ ulimit -Su
2047
$ ulimit -Hu
16384
Check the soft limit for the stack setting. Ensure that the result is in the recommended range. For example:
$ ulimit -Ss
10240
$ ulimit -Hs
32768
/etc/security/limits.conf:
oracle soft nproc 2047
oracle hard nproc 16384
oracle soft nofile 1024
oracle hard nofile 65536
oracle soft stack 10240
Add the following line to the /etc/pam.d/login file, if it does not already exist:
session required pam_limits.so
For the Bourne, Bash, or Korn shell, add the following lines to the /etc/profile file:
if [ $USER = "oracle" ]; then
if [ $SHELL = "/bin/ksh" ]; then
ulimit -p 16384
ulimit -n 65536
else
ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536
fi
fi
|
For the C shell (csh or tcsh), add the following lines to the /etc/csh.login file:
if ( $USER == "oracle" ) then limit maxproc 16384 limit descriptors 65536 endif |
Package Requirements:
binutils-2.20.51.0.2
compat-libcap1-1.10
compat-libcap1-1.10 (32-bit)
compat-libstdc++-33-3.2.3
compat-libstdc++-33-3.2.3 (32 bit)
elfutils-libelf-0.148
elfutils-libelf-devel-0.148
gcc-4.4.4
gcc-c++-4.4.4
glibc-2.12-1
glibc-2.12-1 (32 bit)
glibc-common-2.12
glibc-devel-2.12
glibc-devel-2.12 (32 bit)
glibc-headers-2.12
ksh-20100621
libaio-0.3.107
libaio-0.3.107 (32 bit)
libaio-devel-0.3.107
libaio-devel-0.3.107 (32 bit)
libgcc-4.4.4
libgcc-4.4.4 (32 bit)
libstdc++-4.4.4
libstdc++-4.4.4 (32 bit)
libstdc++-devel-4.4.4
libstdc++-devel-4.4.4 (32 bit)
make-3.81
numactl-devel-2.0.3
sysstat-9.0.4
unixODBC-2.2.14
unixODBC-2.2.14 (32 bit)
unixODBC-devel-2.2.14
unixODBC-devel-2.2.14 (32 bit)
yum install xterm binutils-2*x86_64* compat-libcap1*x86_64* compat-libcap1*i686* compat-libstdc++-33*x86_64* compat-libstdc++-33*i686* elfutils-libelf-0*x86_64* elfutils-libelf-devel-0*x86_64* gcc-4*x86_64* gcc-c++-4*x86_64* glibc-2*x86_64* glibc-2*i686* glibc-devel-2*x86_64* glibc-devel-2*i686* glibc-common-2*x86_64* glibc-headers*x86_64* ksh-*x86_64* libaio-0*x86_64* libaio-0*i686* libaio-devel-0*x86_64* libaio-devel-0*i686* libgcc-4*x86_64* libgcc-4*i686* libstdc++-4*x86_64* libstdc++-4*i686* libstdc++-devel-4*x86_64* libstdc++-devel-4*i686* make-3*x86_64* numactl-devel-2*x86_64* sysstat-9*x86_64* xorg-x11-utils
yum install unixODBC*x86_64* unixODBC*i686* unixODBC-devel*x86_64* unixODBC-devel*i686*
The minimum required RAM for Oracle Database 11g Release 2 running on the Linux platform is 1 GB (although 2 GB or more of RAM is highly recommended).
Use the following command to check the amount of installed RAM on the system:
[root@testnode1 ~]# cat /proc/meminfo | grep MemTotal MemTotal: 4020892 kB |
If the size of the installed RAM is less than the required size, then you must install more memory before continuing.
The following table describes the relationship between installed RAM and the configured swap space recommendation.
| Available RAM | Swap Space Required |
|---|---|
| Between 1 GB and 2 GB | 1.5 times the size of RAM |
| Between 2 GB and 16 GB | Equal to the size of RAM |
| More than 16 GB | 16 GB |
Use the following command to determine the size of the configured swap space:
[root@testnode1 ~]# grep SwapTotal /proc/meminfo SwapTotal: 6258680 kB |
yum install yum-downloadonly
or
yum install yum-plugin-downloadonly
yum update httpd -y --downloadonly --downloaddir=/opt
ls -l /opt/*.rpm
RHEL5 Deployment Guide
https://access.redhat.com/site/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/5/html/Deployment_Guide/ch-swapspace.html
RHEL6 Installation Guide
https://access.redhat.com/site/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/Installation_Guide/s2-diskpartrecommend-x86.html
Oracle DB 10
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/install.102/b15660/pre_install.htm
Oracle DB 11
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/install.112/e24321/pre_install.htm#LADBI1097
БД:
Oracle® Database Installation Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) for Linux x86:
| RAM | Swap Space |
|---|---|
| Between 1024 MB and 2048 MB | 1.5 times the size of RAM |
| Between 2049 MB and 8192 MB | Equal to the size of RAM |
| More than 8192 MB | 0.75 times the size of RAM |
Oracle® Database Installation Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) for Linux:
The following are the memory requirements for installing Oracle Database 11g Release 2 (11.2):
Minimum: 1 GB of RAM
Recommended: 2 GB of RAM or more
# grep MemTotal /proc/meminfo
If the size of the RAM is less than the required size, then you must install more memory before continuing.
Note:
On Linux, the HugePages feature allocates non-swappable memory for large page tables using memory-mapped files. If you enable HugePages, then you should deduct the memory allocated to HugePages from the available RAM before calculating swap space.
| RAM | Swap Space |
|---|---|
| Between 1 GB and 2 GB | 1.5 times the size of the RAM |
| Between 2 GB and 16 GB | Equal to the size of the RAM |
| More than 16 GB | 16 GB |
RHEL5 Deployment Guide:
Table 7.1. Recommended System Swap Space
| Amount of RAM in the System | Recommended Amount of Swap Space |
|---|---|
| 4GB of RAM or less | a minimum of 2GB of swap space |
| 4GB to 16GB of RAM | a minimum of 4GB of swap space |
| 16GB to 64GB of RAM | a minimum of 8GB of swap space |
| 64GB to 256GB of RAM | a minimum of 16GB of swap space |
| 256GB to 512GB of RAM | a minimum of 32GB of swap space |
RHEL6 Installation Guide:
Table 9.2. Recommended System Swap Space
| Amount of RAM in the system | Recommended swap space | Recommended swap space if allowing for hibernation |
|---|---|---|
| ⩽ 2GB | 2 times the amount of RAM | 3 times the amount of RAM |
| > 2GB – 8GB | Equal to the amount of RAM | 2 times the amount of RAM |
| > 8GB – 64GB | 0.5 times the amount of RAM | 1.5 times the amount of RAM |
| > 64GB | 4GB of swap space | No extra space needed |
vi /etc/issue.net
###################################################
# #
# BLA, BLA, BLA! #
# #
# #
###################################################
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
#Banner /some/path
Banner /etc/issue.net
/etc/init.d/sshd restart
touch /var/ntp/ntp.drift
vi /etc/inet/ntp.conf:
server myntpserver.mydomain.ru
driftfile /var/ntp/ntp.drift
svcs -l ntp
svcadm -v enable ntp
ntpq -p
tail -f /var/adm/messages
Troubleshooting:
ntpdate -dv pool.ntp.org
tcpdump dst port 123
yum install nfs* -y
service rpcbind start
service nfs start
service nfslock start
chkconfig rpcbind on
chkconfig nfs on
chkconfig nfslock on
vi /etc/sysconfig/nfs
RQUOTAD_PORT=875
LOCKD_TCPPORT=32803
LOCKD_UDPPORT=32769
MOUNTD_PORT=892
STATD_PORT=662
STATD_OUTGOING_PORT=2020
rpcinfo -p
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m udp -p udp –dport 2049 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m tcp -p tcp –dport 2049 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m udp -p udp –dport 111 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m tcp -p tcp –dport 111 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m udp -p udp –dport 32769 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m tcp -p tcp –dport 32803 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m udp -p udp –dport 662 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m tcp -p tcp –dport 662 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m udp -p udp –dport 875 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m tcp -p tcp –dport 875 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m udp -p udp –dport 892 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -m tcp -p tcp –dport 892 -j ACCEPT
mkdir /myexport
vi /etc/exports
/myexport 192.168.0.0/24(rw,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check)
# *note /home – shared directory
#192.168.0.0/24 – range of networks NFS permits accesses
#rw – possible to read and write
#sync – synchronize
#no_root_squash – enable root privilege
#no_subtree_check – disable subtree check
/etc/hosts.allow:
#mountd: 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0
#lockd: 192.168.0.1 , 192.168.0.2
#rquotad: 192.168.0.1 , 192.168.0.2
mountd: 192.168.0.1 , 192.168.0.2
#statd: 192.168.0.1 , 192.168.0.2
vi /etc/hosts.deny:
portmap:ALL
lockd:ALL
mountd:ALL
rquotad:ALL
statd:ALL
service rpcbind restart
service nfs restart
service nfslock restart
showmount -e 192.168.0.1
mount -t nfs 192.168.0.1:/data/archive /mnt/archive
nfsstat
“Rather than disable SELinux it is a good idea to configure it to allow remote clients to access files that are exported via NFS share. This is fairly simple and involves setting the SELinux boolean value using the “setsebool” utility. In this example we’ll use the “read/write” boolean but we can also use “nfs_export_all_ro” to allow NFS exports read-only and “use_nfs_home_dirs” to allow home directories to be exported.
# setsebool -P nfs_export_all_rw 1”
Ссылки:
http://mylinuxlife.com/setting-up-nfs-on-rhel-6-iptables-firewall-solution/
http://aaronwalrath.wordpress.com/2011/03/18/configure-nfs-server-v3-and-v4-on-scientific-linux-6-and-red-hat-enterprise-linux-rhel-6/
Рассмотрим пример создания volume
fdisk -l
Диск /dev/sdb: 644.2 ГБ
Создаем новый раздел с ФС LVM (8e), который займёт имеющееся нераспределённое дисковое пространство:
fdisk /dev/sdb
n
p
1
[ENTER]
[ENTER]
Меняем тип раздела на Linux LVM (8e):
t
1
8e
Проверяем:
p
Записали и вышли:
w
Создаем pv, vg, lv и FS:
pvcreate /dev/sdb1
vgcreate vg_data /dev/sdb1
lvcreate -n lv_data -l +100%FREE vg_data
mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/vg_data-lv_data
А теперь представим, что у нас появилось стойкое желание уменьшить размер ФС, а освободившееся пространство использовать для создание нового volume+FS:
ВНИМАНИЕ! Перед уменьшением LVM раздела необходимо уменьшить размер ФС!
e2fsck -f /dev/mapper/vg_data-lv_data
Уменьшаем размер FS до 580G
resize2fs /dev/mapper/vg_data-lv_data 580G
Уменьшаем размер LVM-тома до 582G
lvreduce -L 582G /dev/mapper/vg_data-lv_data
Ресайзим FS до полного размера LVM-тома
resize2fs /dev/mapper/vg_data-lv_data
Создаем lv из освободившегося пространства:
lvcreate -n lv_app -l +100%FREE vg_data
mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/vg_data-lv_app
Проверяем, есть ли установленные ntp rpm пакеты:
rpm -qa | grep -i ntp
Установка:
yum install ntp
либо
zypper install ntp
Добавляем “server” к конфигу
vi /etc/ntp.conf:
server 192.168.0.1
Стартуем ntp демон:
rcntp start
или
/etc/init.d/ntp start
или
service ntp start
Проверка, дебаг:
rcntp status
ntptrace
ntpq -pn
date
netstat -planeu | grep :123
Добавить в “автозагрузку”:
chkconfig ntp on
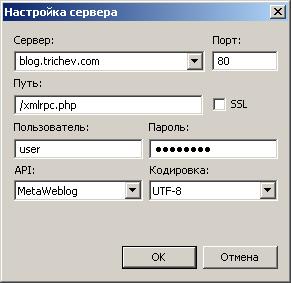
Server: nameofyouserver.com
Port: 80
Path: /xmlrpc.php
SSL –
User: userofblog
Password: youpassword
API: MetaWeblog
Encoding: UTF-8
Installing and Configuring ASMLib **Applies to RHEL 6 and if not setting udev rules:
ASMLib consists of the following components:
An open source (GPL) kernel module package: kmod-oracleasm
An open source (GPL) utilities package: oracleasm-support
A closed source (proprietary) library package: oracleasmlib
Скачать oracleasm-support, oracleasmlib можно здесь – http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/linux/asmlib/rhel6-1940776.html.
‘The kernel driver package ‘kmod-oracleasm’ is available directly from Red Hat, and can be installed from the “RHEL Server Supplementary (v. 6 64-bit x86_64)” channel on Red Hat Network (RHN).’
Способы подписки на RHEL Server Supplementary (v. 6 64-bit x86_64) канал:
1. CLI
rhn-channel –list
rhn-channel –add –channel=rhel-x86_64-server-supplementary-6
rhn-channel –list
2. Red Hat Network Web Interface
Установка пакетов:
rpm -Uhv oracleasmlib-2.0.4-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
rpm -Uhv oracleasm-support-2.1.8-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
yum install kmod-oracleasm
rpm -qa | grep oracleasm
Подготовка дисков:
fdisk -l
fdisk /dev/sdb
n p 1 [ENTER] w
fdisk /dev/sdс
n p 1 [ENTER] w
Проверяем создались ли партиции типа “Linux”:
fdisk -l /dev/sdb
fdisk -l /dev/sdс
Настройка ASMLib:
oracleasm configure
/usr/sbin/oracleasm configure
ORACLEASM_ENABLED=false
ORACLEASM_UID=
ORACLEASM_GID=
ORACLEASM_SCANBOOT=true
ORACLEASM_SCANORDER=””
ORACLEASM_SCANEXCLUDE=””
ORACLEASM_USE_LOGICAL_BLOCK_SIZE=”false”
Настраиваем:
/etc/init.d/oracleasm configure
Default user to own the driver interface [grid]:
Default group to own the driver interface [asmadmin]:
Start Oracle ASM library driver on boot (y/n) [y]:
Scan for Oracle ASM disks on boot (y/n) [y]:
/etc/init.d/oracleasm start
Смотрим что получилось:
oracleasm configure:
ORACLEASM_ENABLED=true
ORACLEASM_UID=grid
ORACLEASM_GID=asmadmin
ORACLEASM_SCANBOOT=true
ORACLEASM_SCANORDER=””
ORACLEASM_SCANEXCLUDE=””
ORACLEASM_USE_LOGICAL_BLOCK_SIZE=”false”
lsmod oracleasm – загружен ли модуль
Именно с правами grid:asmadmin будут создаваться диски в ASMLib.
Создаем диски:
/etc/init.d/oracleasm createdisk ASMDISK01 /dev/sdb1
/etc/init.d/oracleasm createdisk ASMDISK02 /dev/sdc1
Если в процессе создания появится ошибка вида:
‘Marking disk “ASMDISK01” as an ASM disk: [FAILED]’, то в /var/log/oracleasm будет присутствовать “permission denied”, то скорее всего причина этого – включеный в enforcing SELinux.
Проверяем:
getenforce
Если выводит enforcing, то vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux:
SELINUX=permissive или SELINUX=disabled
либо
cat > oracleasm.te << EOF
module oracleasm 1.0;
require {
type unlabeled_t;
class filesystem associate;
}
allow unlabeled_t unlabeled_t:filesystem associate;
EOF
checkmodule -M -m -o oracleasm.mod oracleasm.te
semodule_package -o oracleasm.pp -m oracleasm.mod
semodule -i oracleasm.pp
showdown -r now и заново пробуем создавать диски.
Проверка после создания дисков:
oracleasm listdisks
oracleasm scandisks
ls -l /dev/oracleasm/disks/*
brw-rw—-. 1 grid asmadmin 8, 17 Окт 9 14:07 /dev/oracleasm/disks/ASMDISK01
brw-rw—-. 1 grid asmadmin 8, 33 Окт 9 14:07 /dev/oracleasm/disks/ASMDISK02
Ссылки:
http://et.elostech.cz/docs/en-US/html/Installation_Guide/Subscribing_to_the_Red_Hat_Enterprise_Virtualization_Manager_Channels_using_RHN_Classic.html
https://access.redhat.com/site/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Virtualization/3.0/html/Installation_Guide/Tasks_RHEV_Red_Hat_Network_Subscription.html
http://www.dbaexpert.com/blog/red-hat6-support-for-asmlib/
http://www.dba-oracle.com/t_asm_disk_does_not_exist_or_is_not_instantiated.htm
http://pythianpang.wordpress.com/2009/06/23/initializing-the-oracle-asmlib-driver-failed-selinux-is-turned-on/
http://midba.blogspot.ru/2013/04/redhat-64-comes-with-supporting-asm.html
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/install.112/e17212/storage.htm#CHDFAGJD
https://access.redhat.com/site/articles/216093
http://en.community.dell.com/techcenter/enterprise-solutions/w/oracle_solutions/3336.how-to-deploy-oracle-11gr2-on-rhel6oracle-linux-6.aspx
swapon -s
swapoff /dev/vg_rhel6/lv_swap
lvextend -L +3GB /dev/vg_rhel6/lv_swap
mkswap /dev/vg_rhel6/lv_swap
swapon /dev/vg_rhel6/lv_swap
swapon -s
Ссылки:
http://www.techotopia.com/index.php/Adding_and_Managing_RHEL_6_Swap_Space
После клонирования VMware машины eth0 переименовывается в eth1 и.т.д. Причина такого поведения – одинаковые MAC-адреса.
Правила именования сетевых адаптеров находятся здесь:
/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
vi /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules:
SUBSYSTEM==”net”, ACTION==”add”, DRIVERS==”?*”, ATTR{address}==”11:22:33:44:55:66″, ATTR{type}==”1″, KERNEL==”eth*”, NAME=”eth1″
# PCI device 0x15ad:0x07b0 (vmxnet3)
SUBSYSTEM==”net”, ACTION==”add”, DRIVERS==”?*”, ATTR{address}==”11:22:33:44:55:66″, ATTR{type}==”1″, KERNEL==”eth*”, NAME=”eth0″
Поменял местами только NAME (NAME=”eth0″ -> NAME=”eth1″ у одного и NAME=”eth1″ -> NAME=”eth0″ для второго) у адаптеров.
Далее необходимо поменять MAC-адрес сетевого адаптера в файле /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:
HWADDR=12:34:56:67:78:89
Просмотреть MAC у адаптера, даже если он “опущен”:
ipconfig -a
Перезапуск сетевой системы:
service network restart
Проверяем:
/sbin/ifconfig -a
route -n или netstat -rn
Ссылки:
http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/vmware-linux-lost-eth0-after-cloning-image.html
http://www.banym.de/linux/centos/change-network-device-name-from-eth1-back-to-eth0
Будем считать, что размер диска увеличен в VMware. Теперь требуется провести работы на уровне ОС.
Если необходимо проводить работу без перезагрузки, то нужно пересканировать scsi устройства:
Выводим имена устройств:
ls /sys/class/scsi_device/
0:0:0:0 1:0:0:0 2:0:0:0
Рескан устройства:
echo 1 > /sys/class/scsi_device/0\:0\:0\:0/device/rescan
Если добавляем новый диск:
Вместо рескана уже имеющейся шины scsi, необходимо определить новую шину scsi на хосте.
ls /sys/class/scsi_host/
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 0 Feb 13 02:55 .
drwxr-xr-x 39 root root 0 Feb 13 02:57 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Feb 13 02:57 host0
Рескан хоста:
echo “- – -” > /sys/class/scsi_host/host0/scan
Ищем диск:
fdisk -l Диск /dev/sda: 10.7 ГБ, 10737418240 байт 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders Единицы = цилиндры по 16065 * 512 = 8225280 байт Устр-во Загр Начало Конец Блоки Id Система /dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1044 8281507+ 8e Linux LVM
Обычно это /dev/sda. Создаем новый раздел с ФС LVM (8e), который займёт имеющееся нераспределённое дисковое пространство:
fdisk /dev/sda
Команда (m для справки): n Действие команды e расширенный p основной раздел (1-4) p Номер раздела (1-4): 3 Первый цилиндр (1045-1305, по умолчанию 1045): Используется значение по умолчанию 1045 Последний цилиндр или +size или +sizeM или +sizeK (1045-1305, по умолчанию 1305): Используется значение по умолчанию 1305
Меняем тип файловой системы на LVM:
Команда (m для справки): t Номер раздела (1-4): 3 Шестнадцатеричный код (введите L для получения списка кодов): 8e Системный тип раздела 3 изменен на 8e (Linux LVM) Команда (m для справки): p Диск /dev/sda: 10.7 ГБ, 10737418240 байт 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders Единицы = цилиндры по 16065 * 512 = 8225280 байт Устр-во Загр Начало Конец Блоки Id Система /dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1044 8281507+ 8e Linux LVM /dev/sda3 1045 1305 2096482+ 8e Linux LVM
Записываем таблицу разделов на диск:
Команда (m для справки): w Таблица разделов была изменена! Вызывается ioctl() для перечитывания таблицы разделов. ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ: Перечитывание таблицы разделов завершилось неудачей с ошибкой 16: Устройство или ресурс занято. Ядро все еще использует старую таблицу. Новая таблица будет использована при следующей перезагрузке. Синхронизируются диски. partprobe -s
Если предыдущая команда не проходит, то перезагрузка:
reboot
Преобразуем раздел /dev/sda3 в физический том, чтобы LVM мог использовать его:
pvcreate /dev/sda3 Physical volume "/dev/sda3" successfully created
Добавляем новый физический том в группу томов:
vgextend VolGroup00 /dev/sda3 Volume group "VolGroup00" successfully extended
Выводим информацию о группе томов:
vgdisplay --- Volume group --- VG Name VolGroup00 System ID Format lvm2 Metadata Areas 2 Metadata Sequence No 4 VG Access read/write VG Status resizable MAX LV 0 Cur LV 2 Open LV 2 Max PV 0 Cur PV 2 Act PV 2 VG Size 9,84 GB PE Size 32,00 MB Total PE 315 Alloc PE / Size 252 / 7,88 GB Free PE / Size 63 / 1,97 GB VG UUID AMBRWF-xL1Q-h5vo-cNpH-aix4-ENjR-1VSj29
Группа состоит из двух томов. Первый том относиться к корневой дисковой системе. Второй, размером 1 Гб – swap. Обратите внимание на значение в строке Free PE / Size. Здесь показывается размер свободного дискового пространства доступного группе томов.
Увеличим размер логического тома LogVol00 на всё доступное свободное дисковое пространство в группе:
lvextend -l +100%FREE /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 Extending logical volume LogVol00 to 8,84 GB Logical volume LogVol00 successfully resized
Отображаем информацию о группе томов:
vgdisplay --- Volume group --- VG Name VolGroup00 System ID Format lvm2 Metadata Areas 2 Metadata Sequence No 5 VG Access read/write VG Status resizable MAX LV 0 Cur LV 2 Open LV 2 Max PV 0 Cur PV 2 Act PV 2 VG Size 9,84 GB PE Size 32,00 MB Total PE 315 Alloc PE / Size 315 / 9,84 GB Free PE / Size 0 / 0 VG UUID AMBRWF-xL1Q-h5vo-cNpH-aix4-ENjR-1VSj29
Как видим, группе было выделено все доступное дисковое пространство, но операционная система по-прежнему отображает только старые значения размера файловой системы. Для того чтобы мы могли полностью использовать новое дисковое пространство, нам необходимо изменить размер смонтированной корневой файловой системы на величину размера первого логического тома:
resize2fs -p /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00 resize2fs 1.39 (29-May-2006) Filesystem at /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00 is mounted on /; on-line resizing required Performing an on-line resize of /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00 to 2318336 (4k) blocks. The filesystem on /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00 is now 2318336 blocks long.
Проверяем размер дискового пространства файловой системы:
df -h
Файловая система Разм Исп Дост Исп% смонтирована на
/dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00
8,6G 5,5G 2,7G 68% /
/dev/sda1 99M 12M 82M 13% /boot
tmpfs 506M 0 506M 0% /dev/shm
Размер корневой файловой системы /dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00 увеличился на 2 Гб. Диск VMware расширен до 10 Гб.
Ссылки:
http://alldba.ru/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=247:-vmware&catid=72:vmware&Itemid=61
http://tarhome.com/archives/259
http://mattiasgeniar.be/2010/08/27/increase-a-vmware-disk-size-vmdk-formatted-as-linux-lvm-without-rebooting/
Если при работе в linux в gnome-terminal при нажатии ctrl+x & ctrl+c вылезают русские буквы ч и с и программы не прерываются, то надо в автозагрузку добавить следущую строчку:
setxkbmap -layout us,ru -model pc105 -variant ,winkeys -option grp:ctrl_shift_toggle,terminate:ctrl_alt_bksp
Для этого в Xfce можно открыть графическую утилиту Меню->Настройки->Сеансы и запуск->закладка Автозапуск приложений->кнопка Добавить
Ссылка:
http://nikita-petrov.com/articles/linux-gnome-terminal-vmesto-ctrlx-ctrlc-russkie-bukvy-ch-s
Network layout:
Internet === Router (192.168.0.1) === Debian SRV(192.168.0.2, GW 192.168.0.1, DNS 192.168.0.1)
apt-get install openswan xl2tpd ppp
/etc/ipsec.conf:
version 2.0
config setup
plutostderrlog=/var/log/ipsec.log
nat_traversal=yes
virtual_private=%v4:!10.0.0.0/24
oe=off
protostack=netkey
conn %default
forceencaps=yes
compress=yes
conn l2tp-psk-nat
rightsubnet=vhost:%priv
also=l2tp-psk-nonat
conn l2tp-psk-nonat
authby=secret
pfs=no
auto=add
keyingtries=3
rekey=no
dpddelay=40
dpdtimeout=130
dpdaction=clear
keyexchange=ike
ikelifetime=8h
keylife=1h
type=transport
left=192.168.0.2
leftprotoport=17/1701
leftnexthop=192.168.0.1
right=%any
rightprotoport=17/%any
/etc/ipsec.secrets:
192.168.0.2 %any : PSK “very-secret-key”
/etc/xl2tpd/xl2tpd.conf:
[global]
; listen-addr = 192.168.0.2
; port = 1701
ipsec saref = yes
debug tunnel = yes
debug avp = yes
debug network = yes
debug packet = yes
debug state = yes
force userspace = yes
;
[lns default] ; Our fallthrough LNS definition
ip range = 10.0.0.10-10.0.0.100 ; * Allocate from this IP range
assign ip = yes
local ip = 10.0.0.1 ; * Our local IP to use
length bit = yes ; * Use length bit in payload?
require chap = yes ; * Require CHAP auth. by peer
refuse pap = yes ; * Refuse PAP authentication
require authentication = yes ; * Require peer to authenticate
; name = l2tpVPN ; * Report this as our hostname
ppp debug = yes ; * Turn on PPP debugging
pppoptfile = /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd
/etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd:
ms-dns 8.8.8.8
require-mschap-v2
asyncmap 0
logfile /var/log/xl2tpd.log
noccp
auth
crtscts
lock
hide-password
modem
mru 1280
mtu 1280
debug
nodefaultroute
name l2tpd
proxyarp
lcp-echo-interval 30
lcp-echo-failure 4
ipcp-accept-local
ipcp-accept-remote
noipx
idle 1800
connect-delay 5000
/etc/ppp/chap-secrets:
test l2tpd “testpassword” *
Windows XP/7(reboot after add value):
iptables(VPN):
iptables -A INPUT -m policy –dir in –pol ipsec -p udp –dport 1701 -j ACCEPT # на 1701 пускаем только ipsec пакеты
iptables -A INPUT -p 50 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p udp –dport 500 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p udp –dport 4500 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A FORWARD -i ppp+ -p all -m state –state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT #для общения вне своего ppp
iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o ppp+ -m state –state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE # маскарадим под IP сервера
iptables (router):
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -p udp -m udp –dport 500 -j DNAT –to-destination 192.168.0.1:500
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -p udp -m udp –dport 4500 -j DNAT –to-destination 192.168.0.1:4500
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -p udp -m udp –dport 1701 -j DNAT –to-destination 192.168.0.1:1701
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -p 50 -j DNAT –to-destination 192.168.0.1
В Windows в ключе реестра (указан ниже) необходимо создать DWORD параметр AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule и установить ему значение 2.
•для Windows XP — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\IPsec
•для Windows Vista/7 — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent
По-умолчанию VPN-соединение в windows xp/7 ставит основной маршрут через VPN сеть. Чтобы это изменить необходимо убрать галочку:
Свойства VPN-соединения-Сеть-Протокол Интернета TCP/IP-Свойства-Дополнительно
“Использовать основной шлюз в удаленной сети”. DNS можно тоже выставить вручную, чтобы по-умолчанию брался из уже имеющегося локального подключения.
Ссылки:
http://blog.bertelsen.co/2012/02/debian-squeeze-l2tpipsec-vpn-server.html
http://blog.riobard.com/2010/04/30/l2tp-over-ipsec-ubuntu
http://rootmanager.com/ubuntu-ipsec-l2tp-windows-domain-auth/setting-up-openswan-xl2tpd-with-native-windows-clients.html
http://wiki.debian.org/HowTo/iPhoneVPNServer
http://wingloon.com/2012/01/11/how-to-install-setup-l2tp-over-ipsec-vpn-in-debian-lenny/
http://blackpenguins.ru/?p=151
http://louwrentius.com/blog/2011/12/setting-up-a-vpn-with-your-iphone-using-l2tp,-ipsec-and-linux/
http://www.alsigned.ru/?p=836
https://www.openswan.org/projects/openswan/wiki/L2TPIPsec_configuration_using_openswan_and_xl2tpd
http://www.linux.org.ru/forum/admin/8189019
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;q281555
http://confoundedtech.blogspot.ru/2011/08/android-nexus-one-ipsec-psk-vpn-with.html
http://www.vpnfortress.com/setup/android-l2tp-setup.html
http://www.mayrhofer.eu.org/l2tp-ipsec-gateway-for-mobile-phones
http://unixadmins.su/index.php?topic=1282.0
http://www.lostbyte.com/projects/l2tpipsec-vpn-for-ios/
http://www.jacco2.dds.nl/networking/linux-l2tp.html
http://en.gentoo-wiki.com/w/index.php?title=IPsec_L2TP_VPN_server
http://www.aa-asterisk.org.uk/index.php/Setting_up_an_L2TP/IPSec_server_on_Debian
apt-get install nfs-common portmap nfs-kernel-server
vi /etc/exports:
/home 192.168.0.0/24(rw,sync,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check)
# *note /home ⇒ shared directory
#10.0.0.0/24 ⇒ range of networks NFS permits accesses
#rw ⇒ possible to read and write
#sync ⇒ synchronize
#no_root_squash ⇒ enable root privilege
#no_subtree_check ⇒ disable subtree check
IPTABLES:
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -p udp –dport 111 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -p tcp –dport 111 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -p udp –dport 2049 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -p tcp –dport 2049 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -p udp –dport 32764:32769 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1 -m state –state NEW -p tcp –dport 32764:32769 -j ACCEPT
Дополнительная секурность
/etc/hosts.deny:
lockd:ALL
mountd:ALL
rquotad:ALL
statd:ALL
/etc/hosts.allow:
lockd: 192.168.0.1 , 192.168.0.2
rquotad: 192.168.0.1 , 192.168.0.2
mountd: 192.168.0.1 , 192.168.0.2
statd: 192.168.0.1 , 192.168.0.2
/etc/init.d/portmap start
/etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server start
/etc/init.d/nfs-common start
Запускаем, проверяем (showmount -e 192.168.0.1). Да, не работает. А не работает, т.к. порты открываются старшие и хаотично. Смотрим что открыто rpcinfo -p. Нужно теперь все это хозяйство привести к виду –dport 32764:32769.
Открываем Debian SecuringNFS WIKI:
# /etc/default/nfs-common
STATDOPTS=”–port 32765 –outgoing-port 32766″
# /etc/default/nfs-kernel-server
RPCMOUNTDOPTS=”-p 32767″
# /etc/default/quota
RPCRQUOTADOPTS=”-p 32769″
# /etc/modprobe.d/local.conf
options lockd nlm_udpport=32768 nlm_tcpport=32768
options nfs callback_tcpport=32764
Все опять перегружаем. Для успокоения души смотрим, что порты открылись именно те, которые мы прописали в iptables’ах (rpcinfo -p).
Ссылки:
wikipedia.org (NFS)
http://wiki.debian.org/SecuringNFS
http://www.tldp.org/HOWTO/NFS-HOWTO/
http://www.tldp.org/HOWTO/NFS-HOWTO/security.html
http://www.tldp.org/HOWTO/NFS-HOWTO/server.html
http://24may.kharkov.ua/page65.html
http://www.crazysquirrel.com/computing/debian/servers/nfs.jspx
http://mohado.narod.ru/ru/nfs.html
Все как обычно… Есть несколько LUNов, HBA-адаптер, хранилово предположительно EMC Clariion VNX5700, RHEL6. Сразу все красиво не завелось, но это не так страшно…
Важный файлик:
/usr/share/doc/device-mapper-multipath-0.4.9/multipath.conf.defaults
multipath.conf:
defaults {
find_multipaths yes
user_friendly_names yes
}
blacklist {
wwid “WWID”
devnode “^(ram|raw|loop|fd|md|dm-|sr|scd|st)[0-9]*”
devnode “^hd[a-z]”
devnode “^cciss!c[0-9]d[0-9]*”
}
devices {
# Configurazione specifica EMC CLARiiON
device {
vendor “DGC”
product “*”
product_blacklist “LUNZ”
getuid_callout “/lib/udev/scsi_id –whitelisted –device=/dev/%n”
features “1 queue_if_no_path”
hardware_handler “1 alua”
path_selector “round-robin 0”
path_grouping_policy group_by_prio
failback immediate
rr_weight uniform
no_path_retry 60
rr_min_io 1000
prio alua
}
}
chkconfig multipathd on
service multipathd start
multipath -ll
Полезные команды:
mpathconf
multipath -F
Ссылки:
http://www.nxnt.org/2010/08/multipath-linux-and-emc-clariion/
http://www.sourceware.org/lvm2/wiki/MultipathUsageGuide
https://access.redhat.com/knowledge/docs/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/DM_Multipath/
https://access.redhat.com/knowledge/docs/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/Storage_Administration_Guide
Задача: авторизоваться на сайте и получить информацию.
function get_info($email,$pass)
{
$ch = curl_init();
$url = ‘https://www.somesite.com/login’;
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $url ); // отправляем на
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HEADER, 0); // пустые заголовки
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, 1); // возвратить то что вернул сервер
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION, 1); // следовать за редиректами
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_CONNECTTIMEOUT, 30);// таймаут
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER, false);// просто отключаем проверку сертификата
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_COOKIEJAR, dirname(__FILE__).’/cookies.txt’); // сохранять куки в файл
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_COOKIEFILE, dirname(__FILE__).’/cookies.txt’);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, 1); // использовать данные в post
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, array(
’email’=>$email,
‘password’=>$pass,
));
$data1 = curl_exec($ch);
# curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, ‘http://www.somesite.com/info/index.php?ID=12345’ );
# curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, 0);
# $data2 = curl_exec($ch);
}
get_info(‘mail@mail.com’,’password’);
Здесь все просто, но есть несколько моментов заслуживающих упоминания:
CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION, 1 – работает если PHP в незащищенном режиме и не установлена директива open_basedir. Тоже самое касается директорий для печенек!
Комменты, которые я оставил в тексте показывают как можно дальше работать, уже после авторизации и записи печенек.
Функция тупая, можно добавить проверку на авторизацию поиском на странице logout и т.д.
Ссылки:
http://xdan.ru/avtorizacija-na-sajte-pri-pomoshhi-curl-php.html
http://www.php.net/manual/ru/book.curl.php
http://www.php.net/manual/ru/function.curl-setopt.php